
| Algorithm name | Algorithm description | |
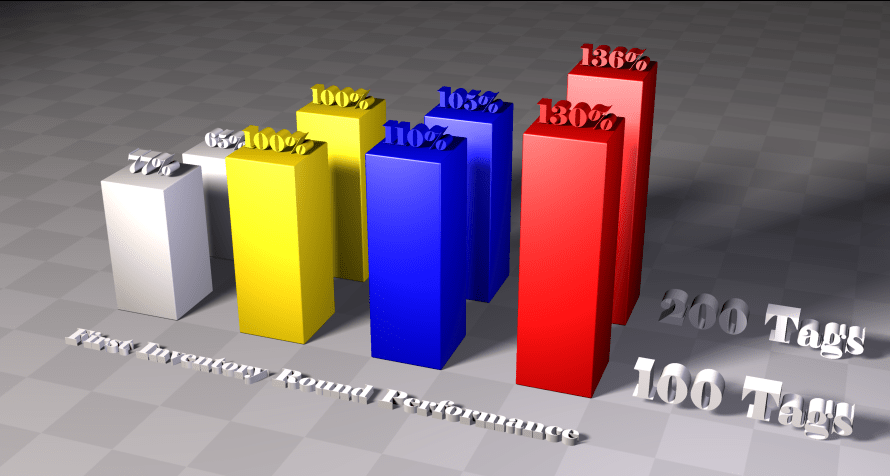
| Standard fixed Q anti-collision algorithm | *The standard algorithm of the 18000-6C protocol. *Performance is significantly reduced when the number of tags is large. *When the number of labels is small, it is not efficient. |
|
| Impinj Dynamic Q anti-collision algorithm | *American IMPINJ company's algorithm *Good efficiency when the number of labels is large or small. *A portion of the performance was sacrificed for compatibility. |
|
| I – Search Dynamic Q Anti-Collision Algorithm V1.0 | *Based on the dynamic Q algorithm of the American IMPINJ company. *After optimization, the performance is slightly improved. *This algorithm is used in firmware versions 6.6 and below. |
|
| I – Search Dynamic Q Anti-Collision Algorithm V2.0 | *Based on the dynamic Q algorithm of the American IMPINJ company. *The new data model has greatly improved performance; this algorithm is used in firmware versions 6.7 and above. *The difference from the traditional algorithm can be clearly felt; the performance difference is more obvious when the number of tags is large. |